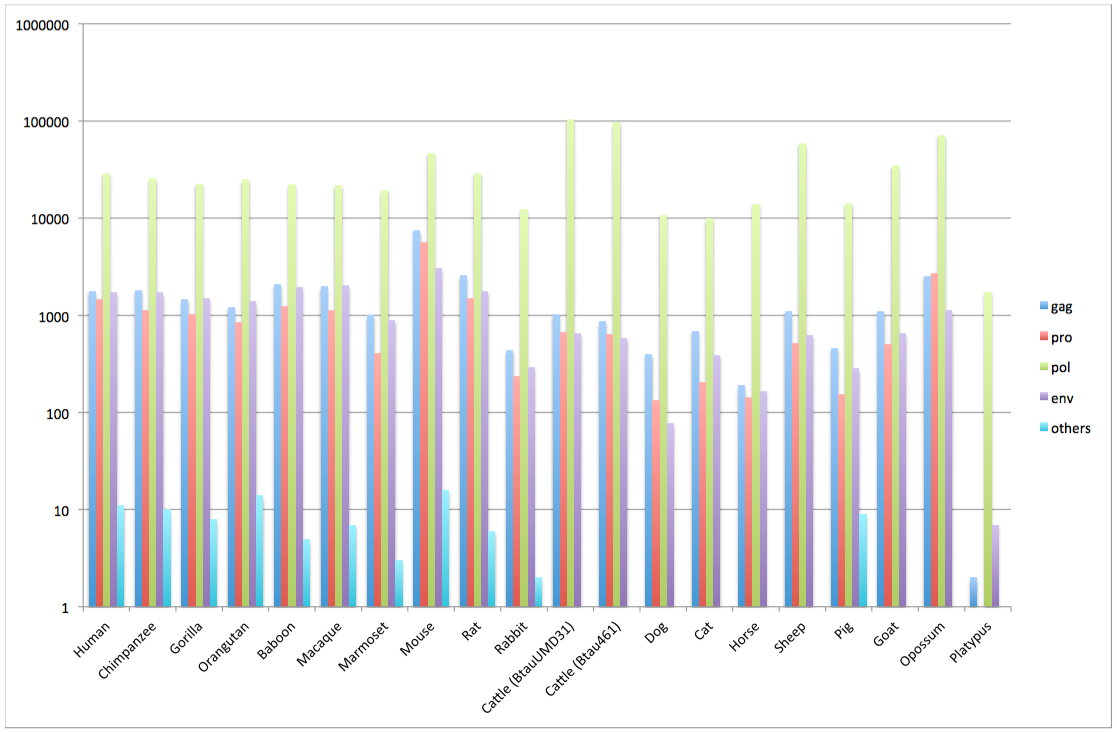
Genome data stored in the gEVE database version 1
| Species | Nomenclature | Genome Database | Genome ID | # of EVEs | # of EVEs (Met)* | HMM profile | ||||
| gag | pro | pol (LINE)** | env | others | ||||||
| Human | Homo sapiens | GRCh38, Dec 2013 | Hsap38 | 33,966 | 31,292 | 1,782 | 1,482 | 29,120 (21,087) | 1,731 | 11 |
| Chimpanzee | Pan troglodytes | CSAC 2.1.4/panTro4, Feb 2011 | Ptro214 | 30,099 | 28,136 | 1,813 | 1,125 | 25,572 (19,043) | 1,719 | 10 |
| Gorilla | Gorilla gorilla gorilla | gorGor3.1/gorGo3, May 2011 | Ggor31 | 26,335 | 24,409 | 1,456 | 1,034 | 22,462 (16,140) | 1,486 | 8 |
| Orangutan | Pongo pygmaeus abelii | PPYG2, Sep 2007 | Pabe2 | 28,315 | 26,716 | 1,214 | 846 | 24,919 (19,492) | 1,400 | 14 |
| Baboon | Papio anubis | Panu_2.0, Jun 2012 | Panu2 | 27,230 | 25,192 | 2,101 | 1,240 | 22,125 (15,476) | 1,962 | 5 |
| Macaque | Macaca mulatta | MMUL 1.0, Feb 2006 | Mmul1 | 26,941 | 25,043 | 1,980 | 1,130 | 21,968 (15,745) | 2,020 | 7 |
| Marmoset | Callithrix jacchus | C_jacchus3.2.1, Jan 2010 | Cjac321 | 21,802 | 20,614 | 992 | 406 | 19,575 (16,070) | 888 | 3 |
| Mouse | Mus musculus | GRCm38.p1, Jan 2012 | Mmus38 | 61,184 | 58,805 | 7,494 | 5,602 | 46,784 (29,122) | 3,075 | 16 |
| Rat | Rattus norvegicus | Rnor_5.0, Mar 2012 | Rnor50 | 34,861 | 32,525 | 2,570 | 1,491 | 29,258 (21,517) | 1,771 | 6 |
| Rabbit | Oryctolagus cuniculus | oryCun2, Nov 2009 | Ocun2 | 13,214 | 12,909 | 438 | 237 | 12,275 (10,473) | 292 | 2 |
| Cow | Bos taurus UMD3.1 | UMD3.1, Dec 2009 | BtauUMD31 | 105,654 | 104,674 | 1,023 | 673 | 103,402 (98,952) | 648 | 1 |
| Cow | Bos taurus 4.6.1 | Btau_4.6.1 Nov 2011 | Btau461 | 98,016 | 97,150 | 860 | 641 | 96,065 (92,153) | 585 | 0 |
| Dog | Canis lupus familiaris | CanFam3.1, Sep 2011 | Cfam31 | 11,393 | 11,011 | 399 | 135 | 10,815 (10,019) | 78 | 0 |
| Cat | Felis catus | Felis_catus_6.2, Sep 2011 | Fcat62 | 11,132 | 10,625 | 694 | 203 | 9,898 (8,505) | 391 | 1 |
| Horse | Equus caballus | Equ Cab 2, Sep 2007 | Ecab2 | 14,391 | 13,972 | 190 | 142 | 13,904 (12,554) | 167 | 0 |
| Sheep | Ovis aries | Oar_v3.1, 2012/09/24 | Oari31 | 61,093 | 60,184 | 1,099 | 517 | 58,940 (55,274) | 628 | 1 |
| Pig | Sus scrofa | Sscrofa10.2, Aug 2011 | Sscr102 | 15,210 | 14,761 | 456 | 155 | 14,350 (13,207) | 285 | 9 |
| Goat | Capra hircus | CHIR_1.0, Jan 2013 | Chir1 | 37,003 | 36,060 | 1,106 | 508 | 34,797 (31,146) | 653 | 0 |
| Opossum | Monodelphis domestica | monDom5, Oct 2006 | Mdom5 | 77,190 | 73,029 | 2,546 | 2,723 | 71,821 (46,874) | 1,134 | 0 |
| Platypus | Ornithorhynchus anatinus | OANA5, Dec 2005 | Oana5 | 1,742 | 1,365 | 2 | 1 | 1,732 (1,658) | 7 | 0 |
*An EVE sequence containing Methionine that can be utilized as the initiation codon (Note that some EVE ORFs obtained in this study do not have an ATG codon)
**Number shown in parentheses indicates pol genes that were thought to be derived from LINEs, which were annotated as “LINE” by RepeatMasker and/or “YP_073558.1” or “NP_048132.1” by BLASTP against the NCBI Viral Genome Database.
HMM profile distributions for each species
Comparison of EVE identification methods
| Genome ID | species | ReTe ∩ ReMa ∩ Blat | ReTe ∩ ReMa | ReTe ∩ Blat | ReMa ∩ Blat | ReTe | ReMa | Blat | Other |
| Hsap38 | Human | 9,959 | 1 | 143 | 22,790 | 573 | 3 | 496 | 1 |
| Ptro214 | Chimpanzee | 8,121 | 8 | 99 | 20,981 | 459 | 9 | 421 | 1 |
| Ggor31 | Gorilla | 6,998 | 3 | 111 | 18,211 | 362 | 9 | 640 | 1 |
| Pabe2 | Orangutan | 6,130 | 2 | 242 | 21,135 | 379 | 18 | 408 | 1 |
| Panu2 | Baboon | 8,876 | 1 | 153 | 17,233 | 492 | 3 | 471 | 1 |
| Mmul1 | Macaque | 8,289 | 3 | 132 | 17,683 | 440 | 6 | 387 | 1 |
| Cjac321 | Marmoset | 3,949 | 3 | 159 | 16,928 | 305 | 6 | 452 | 0 |
| Mmus38 | Mouse | 25,031 | 14 | 407 | 34,260 | 573 | 26 | 873 | 0 |
| Rnor50 | Rat | 9,691 | 0 | 258 | 23,890 | 404 | 4 | 614 | 0 |
| Ocun2 | Rabbit | 1,875 | 0 | 105 | 10,676 | 88 | 3 | 467 | 0 |
| BtauUMD31 | Cow | 8,183 | 7 | 193 | 95,632 | 618 | 270 | 751 | 0 |
| Btau461 | Cow | 7,242 | 9 | 186 | 89,134 | 566 | 263 | 616 | 0 |
| Cfam31 | Dog | 1,075 | 0 | 92 | 9,948 | 62 | 1 | 215 | 0 |
| Fcat62 | Cat | 1,545 | 1 | 674 | 8,259 | 105 | 1 | 547 | 0 |
| Ecab2 | Horse | 1,213 | 1 | 41 | 12,602 | 129 | 2 | 403 | 0 |
| Oari31 | Sheep | 1,789 | 5 | 84 | 57,672 | 207 | 158 | 1,178 | 0 |
| Sscr102 | Pig | 1,505 | 0 | 45 | 13,138 | 104 | 1 | 417 | 0 |
| Chir1 | Goat | 4,026 | 5 | 274 | 31,105 | 431 | 158 | 1,004 | 0 |
| Mdom5 | Opossum | 17,972 | 1,159 | 335 | 54,040 | 903 | 1,581 | 1,200 | 0 |
| Oana5 | Platypus | 39 | 0 | 2 | 1,601 | 0 | 10 | 90 | 0 |
| SUM | – | 133,508 | 1,222 | 3,735 | 576,918 | 7,200 | 2,532 | 11,650 | 6 |
*ReTe, RetroTector; ReMa, RepeatMasker
Methods
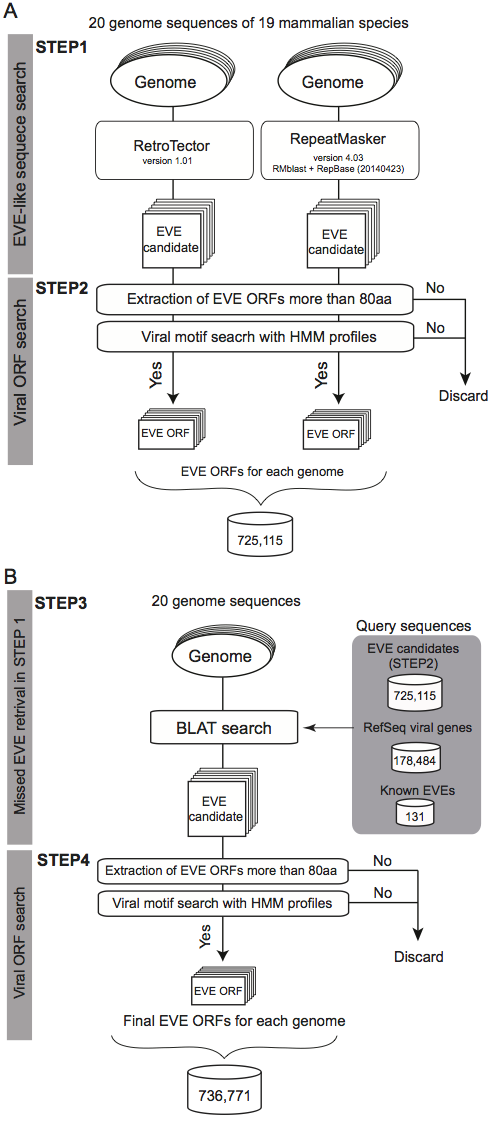
A schematic workflow of a four-step procedure for identifying EVE ORFs in 20 mammalian genomes
STEP1
- 20 mammalian genome sequences were analyzed using two well-known programs for identification of EVE candidate regions.
- RetroTector version 1.0.1
- Repeat Masker version 4.03 with RMblast + RepBase (20140423)
STEP2
- Six possible reading frames (ORF) coding more than 80 aa from EVE sequences (+100 bp at both ends) in both strands were scanned.
- In this database, EVE ORF may not start with ATG codon
- For the EVE candidate ORFs, hmmer3 search using HMM profiles of viral proteins (shown below) were performed.
- Pfam (39 profiles)
- gag (8)
- Gag_p24, Gag_p30, zf-CCHC, zf-CCHC_2, zf-CCHC_3, zf-CCHC_4, zf-CCHC_5, zf-CCHC_6
- pro (23)
- Asp, Asp_protease, Asp_protease_2, Cytomega_UL84, DCD, DUF1758, DUF570, G-patch, G-patch_2, Herpes_ORF11, Herpes_U55, Herpes_UL82_83, Peptidase_A2B, Peptidase_A2E, Peptidase_A3, RVP, RVP_2, Spuma_A9PTase, TAXi_C, TAXi_N, Zn_protease, dUTPase, gag-asp_proteas
- pol (6)
- IN_DBD_C, Integrase_Zn, RNase_H, RVT_1, RVT_thumb, rve
- env (2)
- GP41, TLV_coat
- gag (8)
- GypsyDB (304 profiles)
- gag
- Gag (51)
- GAG_412_mdg1, GAG_alpharetroviridae, GAG_athila, GAG_betaretroviridae, GAG_cer2_3, GAG_crm, GAG_reina, GAG_del, GAG_galadriel, GAG_deltaretroviridae, GAG_gammaretroviridae, GAG_lentiviridae, GAG_micropia_mdg3, GAG_osvaldo, GAG_spumaretroviridae, GAG_tat, GAG_TF, GAG_csrn1, GAG_1731, GAG_17_6, GAG_a_clade, GAG_b_clade, GAG_bel, GAG_codi_c, GAG_codi_d, GAG_codi_I, GAG_codi_II, GAG_copia, GAG_epsilonretroviridae, GAG_galea, GAG_gmr1, GAG_gypsy, GAG_hydra, GAG_maggy, GAG_oryco, GAG_pao, GAG_pCretro, GAG_pseudovirus, GAG_pyggy, GAG_pyret, GAG_retrofit, GAG_sinbad, GAG_sire, GAG_suzu, GAG_tas, GAG_tork, GAG_v_clade, GAGCOAT_caulimovirus, GAGCOAT_cavemovirus, GAGCOAT_soymovirus, GAGCOAT_badnavirus
- Protease (62)
- AP_DTG_ILG_template, AP_micropia_mdg3, AP_alpharetroviridae, AP_athila, AP_betaretroviridae, AP_cer2_3, AP_bel, AP_crm, AP_reina, AP_del, AP_galadriel, AP_cog3577, AP_cog5550, AP_ddi, AP_deltaretroviridae, AP_gammaretroviridae, AP_lentiviridae, AP_nix1, AP_osvaldo, AP_pepsins_A1a, AP_pepsins_A1b, AP_saspase, AP_retropepsins, AP_spumaretroviridae, AP_tat, AP_ty1copia, AP_csrn1, AP_1731, AP_17_6, AP_412_mdg1, AP_a_clade, AP_b_clade, AP_caulimoviridae_dom2, AP_caulimovirus, AP_badnavirus, AP_cavemovirus, AP_codi_c, AP_codi_d, AP_codi_I, AP_codi_II, AP_copia, AP_epsilonretroviridae, AP_galea, AP_gmr1, AP_gypsy, AP_hydra, AP_maggy, AP_oryco, AP_pao, AP_pseudovirus, AP_pyggy, AP_pyret, AP_pCretro, AP_retrofit, AP_sinbad, AP_sire, AP_soymovirus, AP_suzu, AP_tas, AP_TF, AP_tork, AP_v_clade
- Reverse_Transcriptase (51)
- RT_412_mdg1, RT_alpharetroviridae, RT_athila, RT_betaretroviridae, RT_cer2_3, RT_crm, RT_reina, RT_del, RT_galadriel, RT_TF, RT_deltaretroviridae, RT_gammaretroviridae, RT_lentiviridae, RT_micropia_mdg3, RT_osvaldo, RT_spumaretroviridae, RT_tat, RT_csrn1, RT_1731, RT_17_6, RT_a_clade, RT_b_clade, RT_badnavirus, RT_bel, RT_caulimovirus, RT_cavemovirus, RT_codi_c, RT_codi_d, RT_codi_I, RT_codi_II, RT_copia, RT_epsilonretroviridae, RT_galea, RT_gmr1, RT_gypsy, RT_hydra, RT_maggy, RT_oryco, RT_pao, RT_pCretro, RT_pseudovirus, RT_pyggy, RT_pyret, RT_retrofit, RT_sinbad, RT_sire, RT_soymovirus, RT_suzu, RT_tas, RT_tork, RT_v_clade
- Ribonuclease_H (51)
- RNaseH_412_mdg1, RNaseH_alpharetroviridae, RNaseH_athila, RNaseH_betaretroviridae, RNaseH_cer2_3, RNaseH_crm, RNaseH_reina, RNaseH_del, RNaseH_galadriel, RNaseH_TF, RNaseH_deltaretroviridae, RNaseH_gammaretroviridae, RNaseH_lentiviridae, RNaseH_micropia_mdg3, RNaseH_osvaldo, RNaseH_spumaretroviridae, RNaseH_tat, RNaseH_csrn1, RNaseH_1731, RNaseH_17_6, RNaseH_a_clade, RNaseH_b_clade, RNaseH_badnavirus, RNaseH_bel, RNaseH_caulimovirus, RNaseH_cavemovirus, RNaseH_codi_c, RNaseH_codi_d, RNaseH_codi_I, RNaseH_codi_II, RNaseH_copia, RNaseH_epsilonretroviridae, RNaseH_galea, RNaseH_gmr1, RNaseH_gypsy, RNaseH_hydra, RNaseH_maggy, RNaseH_oryco, RNaseH_pao, RNaseH_pCretro, RNaseH_pseudovirus, RNaseH_pyggy, RNaseH_pyret, RNaseH_retrofit, RNaseH_sinbad, RNaseH_sire, RNaseH_soymovirus, RNaseH_suzu, RNaseH_tas, RNaseH_tork, RNaseH_v_clade
- Integrase (48)
- INT_412_mdg1, INT_alpharetroviridae, INT_athila, INT_betaretroviridae, INT_cer2_3, INT_crm, INT_reina, INT_del, INT_galadriel, INT_TF, INT_deltaretroviridae, INT_gammaretroviridae, INT_lentiviridae, INT_micropia_mdg3, INT_osvaldo, INT_spumaretroviridae, INT_tat, INT_csrn1, GIN1, INT_1731, INT_17_6, INT_a_clade, INT_b_clade, INT_bel, INT_codi_c, INT_codi_d, INT_codi_I, INT_codi_II, INT_copia, INT_epsilonretroviridae, INT_galea, INT_gmr1, INT_gypsy, INT_hydra, INT_maggy, INT_oryco, INT_pao, INT_pCretro, INT_pseudovirus, INT_pyggy, INT_pyret, INT_retrofit, INT_sinbad, INT_sire, INT_suzu, INT_tas, INT_tork, INT_v_clade
- Chromodomain (3)
- CHR_all, CHR_shadow, CHR_retroelement
- Env (13)
- ENV_alpharetroviridae, ENV_athila, ENV_B-type_betaretroviridae, ENV_D-type_betaretroviridae, ENV_deltaretroviridae, ENV_gammaretroviridae, ENV_errantiviridae, ENV_lentiviridae, ENV_retroviridae, ENV_spumaretroviridae, ENV_epsilonretroviridae, ENV_sire, ENV_tas
- dUTPase (3)
- DUT_betaretroviridae, DUT_lentiviridae, DUT_caulimoviruses
- Accessory_proteins (22)
- BEL1_spumaretroviridae, BEL2_spumaretroviridae, NEF_retroviridae, ORFQ_retroviridae, VIF_retroviridae, VIF_Q_retroviridae, ORFW_retroviridae, ORFX_betaretroviridae, REV_retroviridae, REX_retroviridae, ROF_retroviridae, SORF_retroviridae, TAT_retroviridae, TAX_retroviridae, TOF_retroviridae, VPR_VPX_retroviridae, VPR_retroviridae, VPX_retroviridae, ORF2_badnavirus, ORF6_badnavirus, ORFB_soymovirus, ORFC_soymovirus
- Aphid_transmission_factor (1)
- ATF_caulimovirus
- Movement_protein (4)
- MOV_badnavirus, MOV_caulimovirus, MOV_soymovirus, MOV_cavemovirus
- Transactivator/viroplasmin_protein (3)
- TAV_caulimovirus, TAV_cavemovirus, TAV_soymovirus
- Virion_associated_protein (2)
- VAP_caulimovirus, VAP_badnavirus
- Pfam (39 profiles)
STEP3
- 20 genome sequences were scanned by BLAT searches using the following amino acid sequences:
- All EVE sequences identified in the 20 genomes (above mentioned sequences)
- 774,172 sequences(726,934 sequences without duplicates)
- All viral sequences coding proteins stored in the NCBI Viral Genome Database (viral.1.protein.faa, version 07/10, 2014)
- 200,396 sequences (178,484 sequences without duplicates)
- Known EVE sequences coding proteins
- All EVE sequences identified in the 20 genomes (above mentioned sequences)
STEP4
- All BLAT hit sequences were also searched by hmmer3 as shown in the STEP2 and merged all sequences identified RetroTector, Repeat Masker and BLAT
Annotation
We simply applied the BLAST best hit(s) for annotation of each EVE sequence. The relationships among BLAST hits against all viral sequences coding proteins stored in the NCBI Viral Genome Database (viral.1.protein.faa) shown in the database.
Validation
Comparison between known EVE sequences and gEVE IDs were shown in the Google Sheets.
Usage (examples)
RNA-seq analysis
We provide a General Transfer Format (GTF) file for EVE gene loci of each genome stored in the gEVE database (see “Download” page). Using these GTF files with NGS data, dynamic expression profiles of EVE genes can be examined. For example, the RNA-seq data of human placenta expression (ID: ERR315374) stored in the sequence read archive (SRA) were examined. The FASTQ sequences were obtained and mapped onto the human genome (GRCh38) using TopHat2. The expression levels of EVE sequences were computed using Cufflinks with the GTF file of gEVE Hsap38. The top 10 EVE sequences showing biggest FPKM values (i.e. highly expressed EVE sequences) are summarized in Table 3. We successfully identified known EVEs expressed in human placenta — PEG10, suppressyn, syncytin-1 and syncytin-2 — as well as novel EVE sequences. This result shows that NGS data analyses combined with our annotation data enable us to discover hidden functional EVE sequences in genomes.